はじめに はじめまして。Technology Inovation Group (TIG) の原田と申します。
以前はGoを使ってアプリ開発を行っていたのですが、ここ最近はPythonを書くことが多いです。pytest を使うことが多く、その中で「テストケースごとに違うデータを事前準備したい」というモチベーションが発生したので、pytestを使用して実装していきます。
前提 以下の読者を想定しています。
Pythonやpytestは多少触ったことがある
環境構築は完了している
できること
複数のテストケースごとに異なる事前処理・事後処理ができる
事前処理と事後処理を分離してテストコードをスッキリかける
環境
Python 3.12.4
pytest 8.3.3
やってみる ※ツールの導入方法に関しては今回は割愛します。
まずはそれぞれの機能のおさらいをします。
parametrize parametrizeは一言で言うと「テストケースに複数の異なる入力や条件を渡して、同じテスト関数を何度も異なるデータで実行できる機能」です。
例えば、以下のような関数をテストしたいとします。
def add (x, y ): return x + y
これに対して複数の条件のテストを実行するには以下のように記載します。
pytest.paramに指定した変数が先頭から順にテスト関数の変数に渡されるイメージです。
idはテストケースに名前を付けられます。可読性も向上するのでお勧めです。
import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize( ["x" , "y" , "expected" ], [ pytest.param(1 , 2 , 3 , id ="normal1" pytest.param(1 , 4 , 5 , id ="normal2" pytest.param(1 , 4 , 3 , id ="abnormal" ], def test_add (x, y, expected ): assert add(x, y) == expected
これを実行すると以下のように表示されます。
test_main.py::test_add[normal1] PASSED [ 33%] test_main.py::test_add[normal2] PASSED [ 66%] test_main.py::test_add[abnormal] FAILED [100%] ======================================= FAILURES ======================================= __________________________________ test_add[abnormal] __________________________________ x = 1, y = 4, expected = 3 @pytest.mark.parametrize( ["x" , "y" , "expected" ], [ pytest.param(1, 2, 3, id ="normal1" ), pytest.param(1, 4, 5, id ="normal2" ), pytest.param(1, 4, 3, id ="abnormal" ), ], ) def test_add(x, y, expected): > assert add(x, y) == expected E assert 5 == 3 E + where 5 = add(1, 4) test_main.py:67: AssertionError =============================== short test summary info ================================ FAILED test_main.py::test_add[abnormal] - assert 5 == 3
fixture fixtureは一言で言うと「テスト関数の前に特定の状態や環境を準備するための仕組み」です。
yieldを使用するとテスト関数実行後のteardown処理も実行でき、非常に便利です。
例えばDBに事前にデータを投入したい場合を考えます。
import pytest@pytest.fixture def db_setup (): db_client = get_db_client() db_client.insert(some_data) print ("DBデータ投入完了" ) yield db_client db_client.clean_up() print ("DBクリーンアップ完了" )
このfixtureを利用するにはテスト関数に引数として渡してあげます。
def test_hoge_function (db_setup ): print ("テスト対象の関数実行" ) hoge_function(db_setup) result = db_setup.select() assert result == expected
これを実行すると以下のように表示されます。
期待通り、セットアップとクリーンアップが実行されていることが確認できますね。
test_main.py::test_hoge_function FAILED [100%] ======================================= FAILURES ======================================= __________________________________ test_hoge_function __________________________________ db_setup = <clean_crawler.test_main.db object at 0x7f2470358740> def test_hoge_function(db_setup): print ("テスト対象の関数実行" ) result = hoge_function(db_setup) > assert result == expected E AssertionError: assert 'result' == 'expected' E E - expected E + result test_main.py:48: AssertionError -------------------------------- Captured stdout setup --------------------------------- DBデータ投入完了 --------------------------------- Captured stdout call --------------------------------- テスト対象の関数実行 ------------------------------- Captured stdout teardown ------------------------------- DBクリーンアップ完了 =============================== short test summary info ================================ FAILED test_main.py::test_hoge_function - AssertionError: assert 'result' == 'expected'
fixture & parametrize ではいよいよ本題に入ります。
「テストケースごとに違うデータを事前準備したい」という目的ですが、これは「fixtureに対して、parametrizeで異なる変数を渡したい」と言い換えることができます。
fixtureを紹介した時のhoge_functionのテストコードを再掲します。
def test_hoge_function (db_setup ): print ("テスト対象の関数実行" ) result = hoge_function(db_setup) assert result == expected
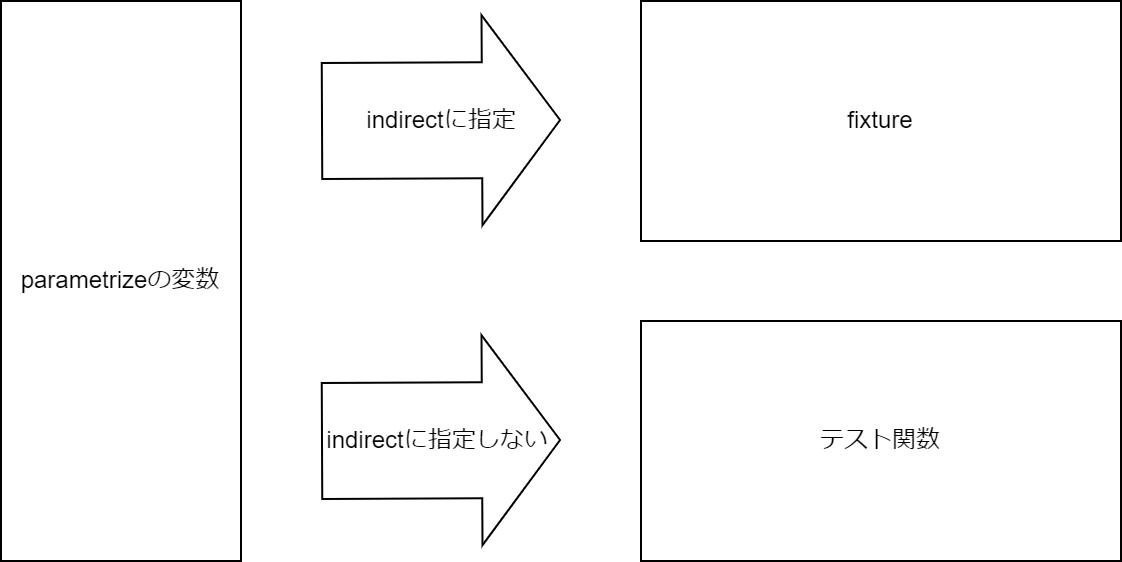
これをparametrize化しましょう。引数にfixture(db_setup)を渡しているので、parameterizeにも同じ変数名を指定します。そして、引数indirectにfixture名を渡します。
テスト関数に直接渡す変数に関しては、indirectに指定しません。
以下の図ようなイメージで変数が渡されます。
重要: fixtureをindirectに指定する
以下の例の場合、db_setupをindirectに指定しているので、テストデータxはfixtureに渡され、「期待値x」はテスト関数に直接渡されます。
import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize( ["db_setup" , "expected" ], [ pytest.param("テストデータ1" , "期待値1" , id ="case1" pytest.param("テストデータ2" , "期待値2" , id ="case2" pytest.param("テストデータ3" , "期待値3" , id ="case3" ], indirect=["db_setup" ] def test_hoge_function (db_setup, expected ): print ("テスト対象の関数実行" ) result = hoge_function(db_setup) assert result == expected
fixtureでparametrizeからの変数を受け取る場合、引数にrequestをとり、request.paramとすることでアクセスすることができます。
重要: parametrizeで渡される変数にアクセスするにはrequest.paramでアクセスする
import pytest@pytest.fixture def db_setup (request ): db_client = get_db_client() print (f"{request.param} が投入されます" ) db_client.insert(request.param) print ("DBデータ投入完了" ) yield db_client db_client.clean_up() print ("DBクリーンアップ完了" )
全てのコードは以下の通りになります。
import pytest@pytest.fixture def db_setup (request ): db_client = get_db_client() print (f"{request.param} が投入されます" ) db_client.insert(request.param) print ("DBデータ投入完了" ) yield db_client db_client.clean_up() print ("DBクリーンアップ完了" ) @pytest.mark.parametrize( ["db_setup" , "expected" ], [ pytest.param("テストデータ1" , "期待値1" , id ="case1" pytest.param("テストデータ2" , "期待値2" , id ="case2" pytest.param("テストデータ3" , "期待値3" , id ="case3" ], indirect=["db_setup" ], def test_hoge_function (db_setup, expected ): print ("テスト対象の関数実行" ) hoge_function(db_setup) result = db_setup.select() assert result == expected
これを実行すると以下のように表示されます。
冗長になるので一部表示を省略していますが、期待通りセットアップとクリーンアップがテストケースごとに実行されていることが確認できますね。
test_main.py::test_hoge_function[case1] FAILED [ 33%] test_main.py::test_hoge_function[case2] FAILED [ 66%] test_main.py::test_hoge_function[case3] FAILED [100%] ============================================ FAILURES ============================================ ___________________________________ test_hoge_function[case1] ____________________________________ ~~<略>~~ E AssertionError: assert 'test_input' == 'expected' test_main.py:102: AssertionError ------------------------------------- Captured stdout setup -------------------------------------- テストデータ1が投入されます DBデータ投入完了 -------------------------------------- Captured stdout call -------------------------------------- テスト対象の関数実行 ------------------------------------ Captured stdout teardown ------------------------------------ DBクリーンアップ完了 ___________________________________ test_hoge_function[case2] ____________________________________ ~~<略>~~ E AssertionError: assert 'test_input' == 'expected' test_main.py:102: AssertionError ------------------------------------- Captured stdout setup -------------------------------------- テストデータ2が投入されます DBデータ投入完了 -------------------------------------- Captured stdout call -------------------------------------- テスト対象の関数実行 ------------------------------------ Captured stdout teardown ------------------------------------ DBクリーンアップ完了 ___________________________________ test_hoge_function[case3] ____________________________________ ~~<略>~~ E AssertionError: assert 'test_input' == 'expected' test_main.py:102: AssertionError ------------------------------------- Captured stdout setup -------------------------------------- テストデータ3が投入されます DBデータ投入完了 -------------------------------------- Captured stdout call -------------------------------------- テスト対象の関数実行 ------------------------------------ Captured stdout teardown ------------------------------------ DBクリーンアップ完了 ==================================== short test summary info ===================================== FAILED test_main.py::test_hoge_function[case1] - AssertionError: assert 'test_input' == 'expected' FAILED test_main.py::test_hoge_function[case2] - AssertionError: assert 'test_input' == 'expected' FAILED test_main.py::test_hoge_function[case3] - AssertionError: assert 'test_input' == 'expected'
まとめ
parametrizeでfixtureに変数を渡す際にはindirectに指定するfixtureでparametrizeから渡される変数にアクセスするにはrequest.paramでアクセスする
parametrizeとfixtureをうまく使用することで、テスト処理と準備処理を分離し、すっきりとした見通しの良いテストコードを整備することができます。
parametrizeとfixtureを同時に使用する際の書き方について少し沼にはまったので、記事にしました。
同じく沼にはまりそうになっている方の一助になれば幸いです。
ここまでご覧いただきありがとうございました。